C#语言入门详解(18)传值、输出、引用、数组、具名、可选参数、扩展方法
- 一、传值参数
- 1. 值类型
- 2. 引用类型,并且创建对象
- 3. 引用类型,不创建对象
- 二、引用参数
- 1. 值类型
- 2. 引用类型,创建新对象
- 3. 引用类型,不创建新对象
- 三、输出形参
- 1. 值类型
- 2. 引用类型
- 四、数组参数
- 五、具名参数
- 六、可选参数
- 七、扩展方法
- 总结
内容来自刘铁猛C#语言入门详解课程。
参考文档:CSharp language specification 5.0 中文版

一、传值参数
1. 值类型
- 声明时不带修饰符的形参是值形参。 一个值形参对应于一个局部变量, 只是它的初始值来自该方法调用所提供的相应实参。
当形参是值形参时, 方法调用中的对应实参必须是表达式, 并且它的类型可以隐式转换为形参的类型。
允许方法将新值赋给值参数。 这样的赋值只影响由该值形参表示的局部存储位置, 而不会影响在方法调用时由调用方给出的实参。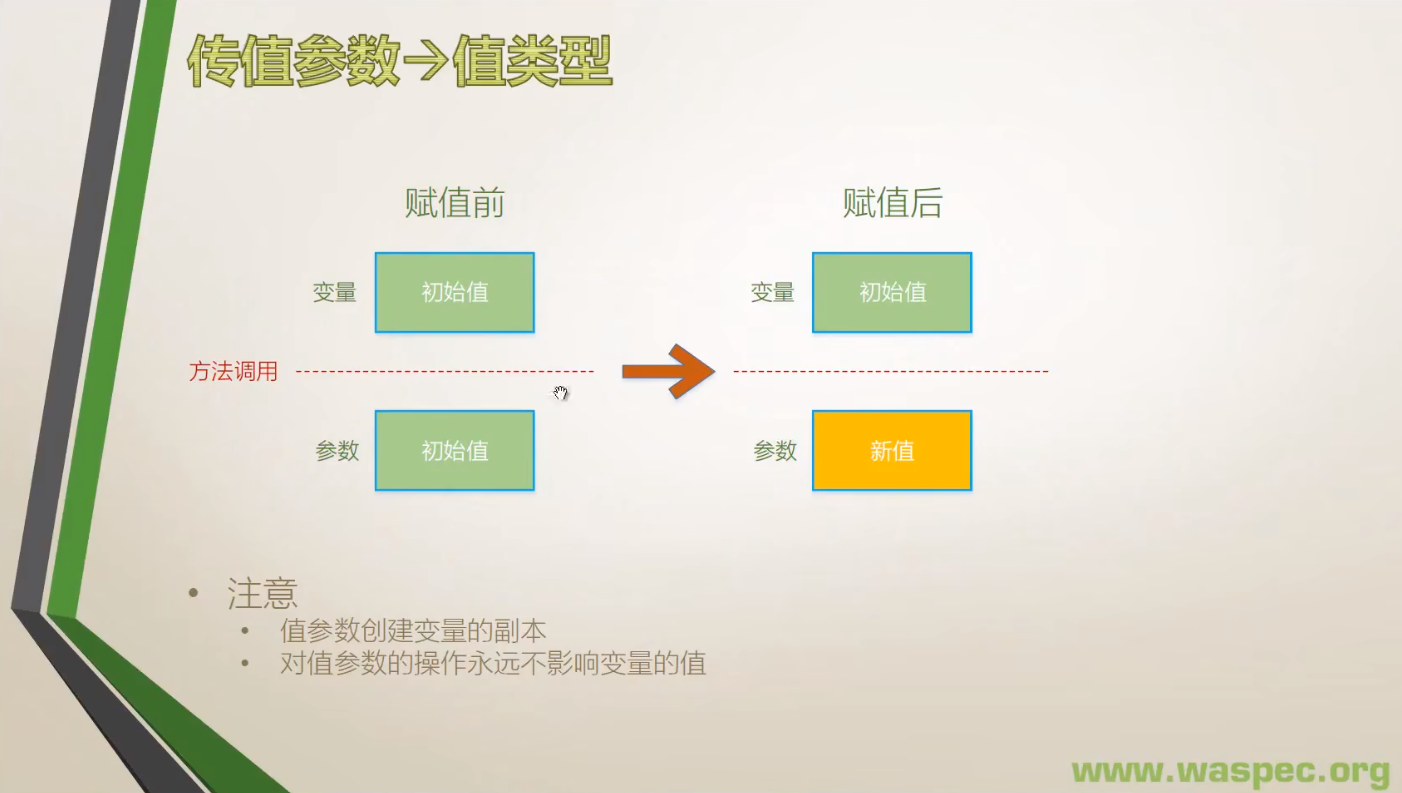
namespace ParametersExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main{
string[] args)
Student stu = new Student()
int y= 100;
stu.AddOne(y);
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
class Student
{
public void AddOne(int x)
x = x+ 1;
Console.WriteLine(x):
}2. 引用类型,并且创建对象
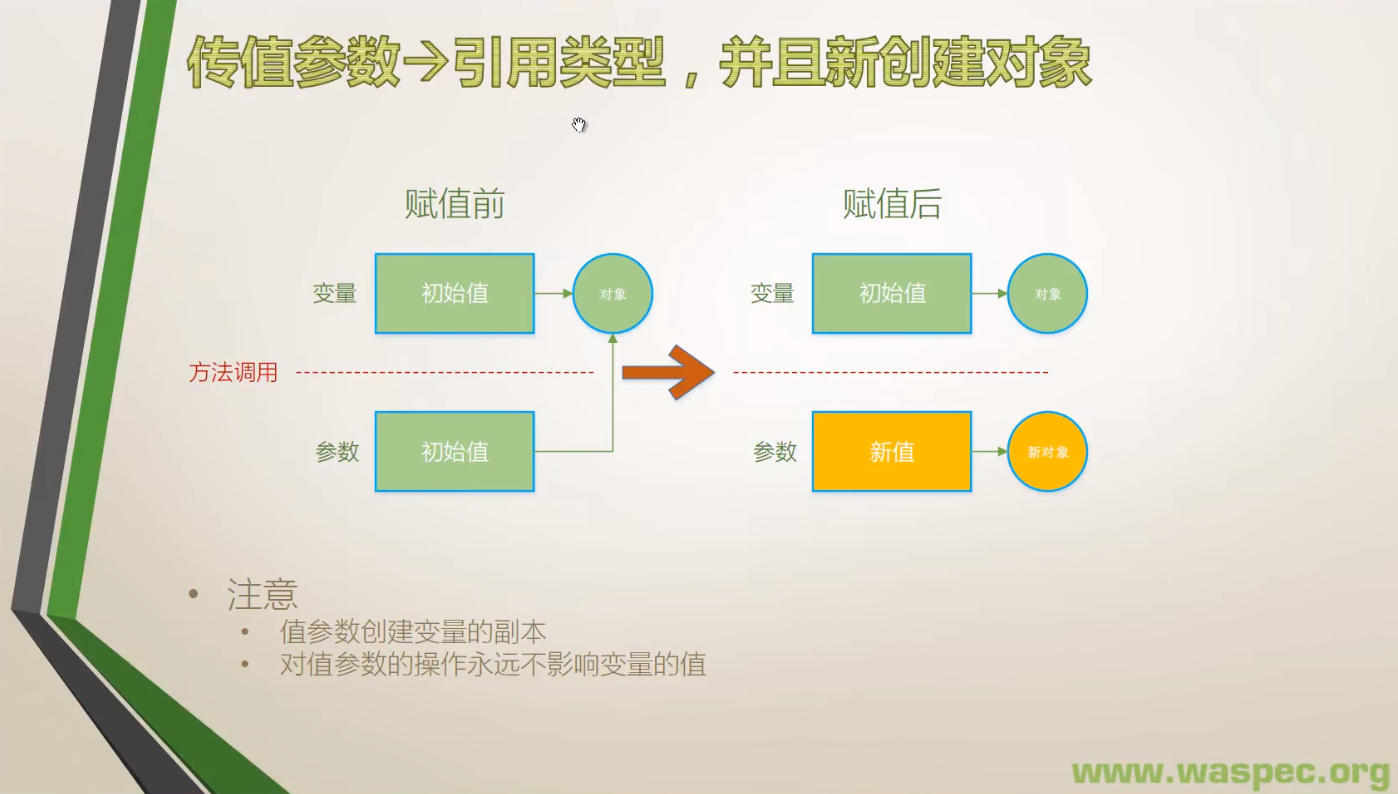
- 引用参数很少使用,一般情况都是传进来引用它的值,而不是连接到新对象去(基本只有面试题会考这个)。
- 注:当参数类型为 string 时,在方法内部修改参数的值,对应的是此处创建对象这种情况。
因为 string 是 immutable 的,所以在方法内部对 string 赋值实际是“创建新的 string 实例再赋值”,最终方法外部的 string 并不会改变。 - Object.GetHashCode() 方法,用于获取当前对象的哈希代码,引每个对象的 Hash Code 都不一样,可通过 Hash Code 来区分两个 Name 相同的 stu 对象。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var stu = new Student() { Name="Tim"
};
SomeMethod(stu);
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
Console.WriteLine(stu.GetHashCode());
}
static void SomeMethod(Student stu)
{
//通过new修改指向地址
stu = new Student { Name = "Tim"
};
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
Console.WriteLine(stu.GetHashCode());
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name {
get;
set;
}
}3. 引用类型,不创建对象
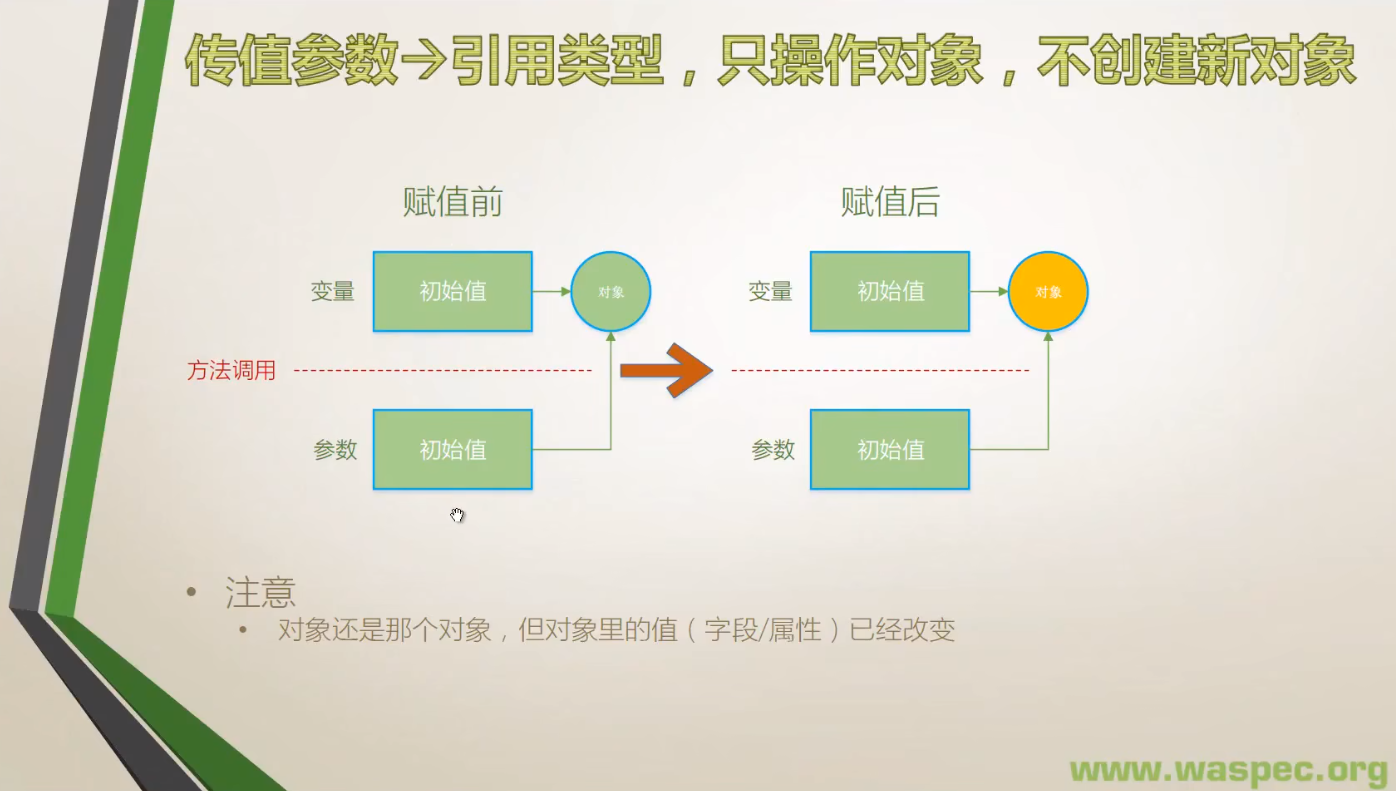
- 这种通过传递进来的参数修改其引用对象的值的情况,在使用中比较少见。因为作为方法,其主要输出还是靠返回值。我们把这种修改参数所引用对象的值的操作叫做方法的副作用(side-effect),这种副作用平时编程时要尽量避免。
namespace ParametersExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student() { Name = "Tim”
};
UpdateObject(stu);
Console.WriteLine["HashCode={0}, Name-{1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
static void UpdateObject(Student stu)
{
stu.Name="Tom";
//副作用,side-effect
Console.WriteLine["HashCode-{0}, Name={1}", stu.GetHashCodel), stu.Name);
}
}
}二、引用参数
1. 值类型
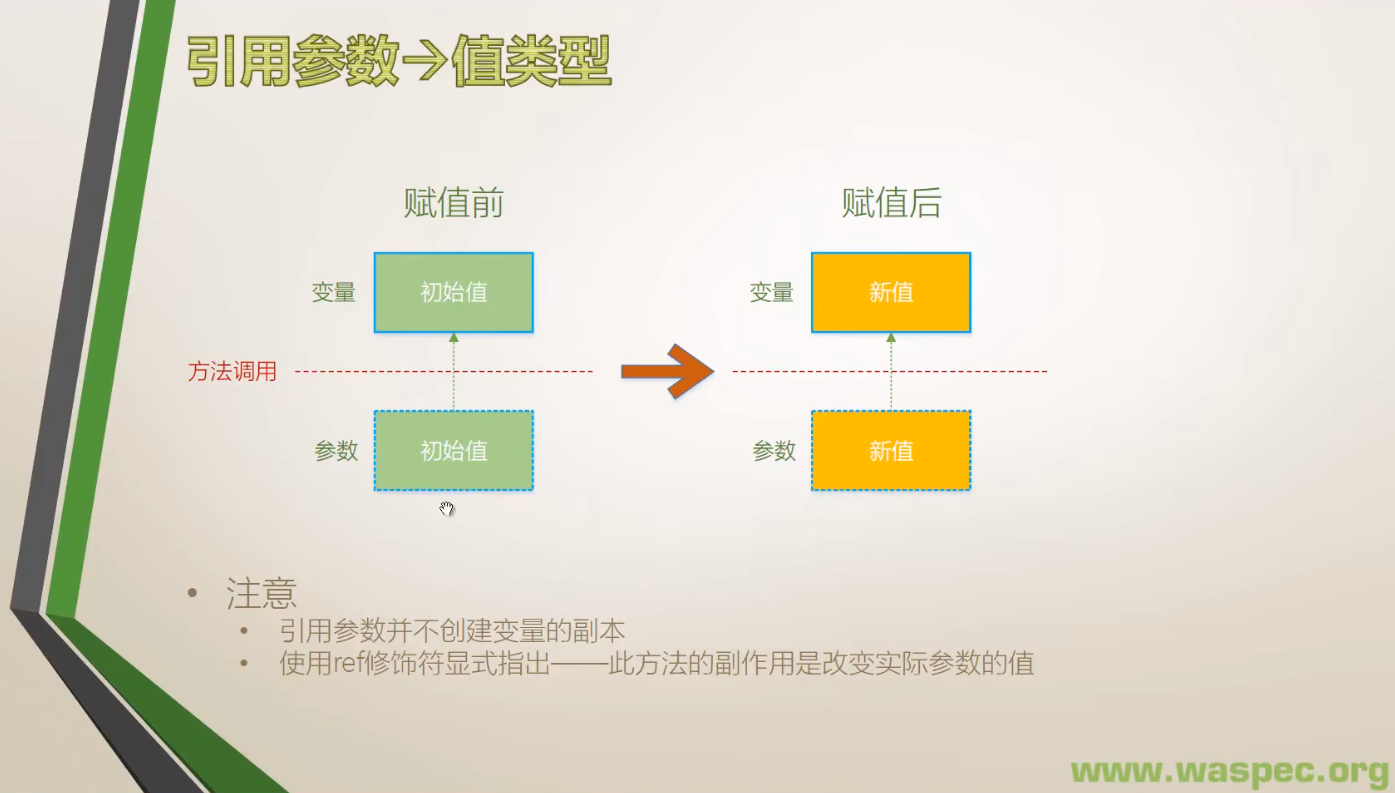
- 引用形参是用 ref 修饰符声明的形参。 与值形参不同, 引用形参并不创建新的存储位置。相反,引用形参表示的存储位置恰是在方法调用中作为实参给出的那个变量所表示的存储位置。
- 当形参为引用形参时,方法调用中的对应实参必须由关键字 ref 并后接一个与形参类型相同的 variablereference组成。 变量在可以作为引用形参传递之前, 必须先明确赋值。
- 在方法内部, 引用形参始终被认为是明确赋值的。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int y = 1;
IWantSideEffect(ref y);
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref int x)
{
x += 100;
}2. 引用类型,创建新对象
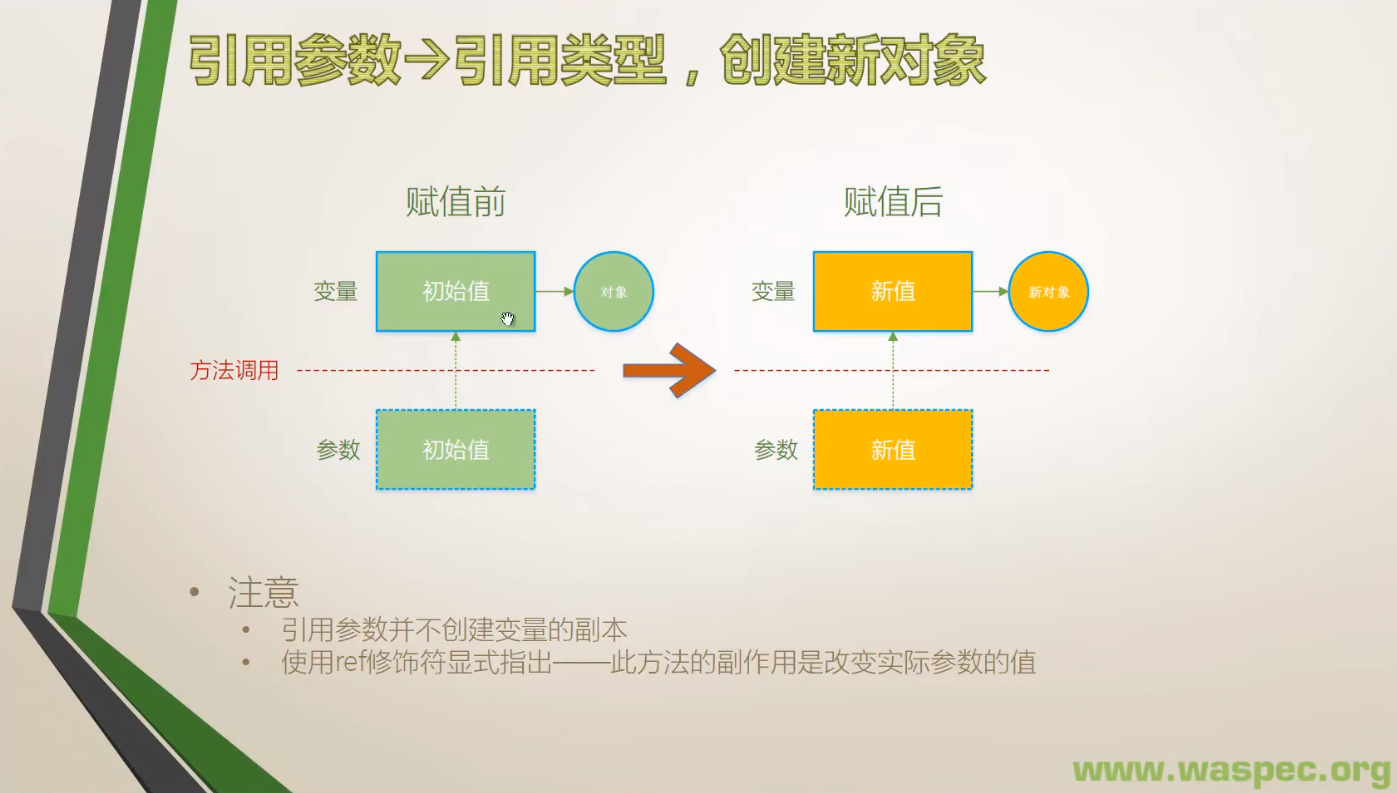
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var outterStu = new Student() { Name = "Tim"
};
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0}, Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);
Console.WriteLine("-----------------");
IWantSideEffect(ref outterStu);
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0}, Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref Student stu)
{
stu = new Student() { Name = "Tom"
};
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0}, Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name {
get;
set;
}
}
3. 引用类型,不创建新对象
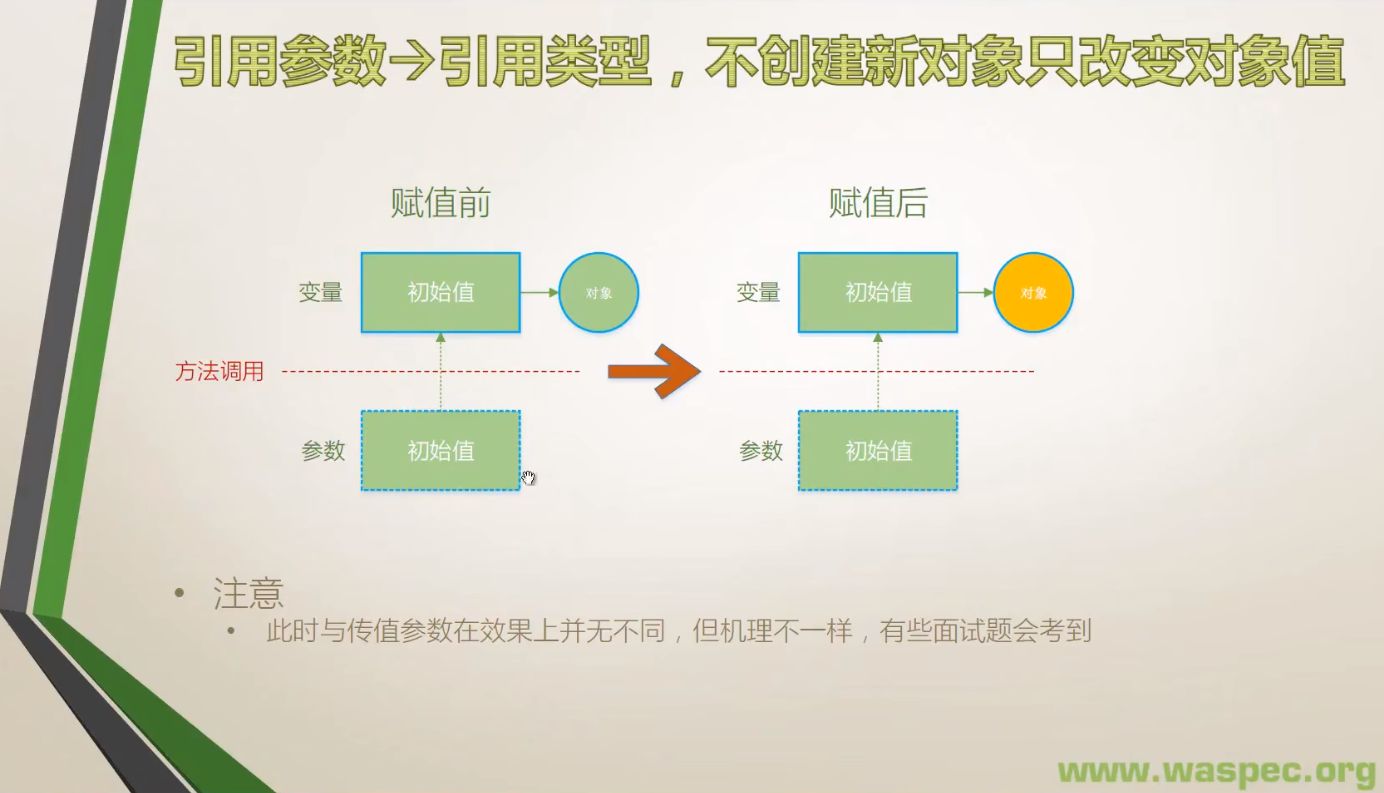
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var outterStu = new Student() { Name = "Tim"
};
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0}, Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);
Console.WriteLine("-----------------");
SomeSideEffect(ref outterStu);
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0}, Name={1}", outterStu.GetHashCode(), outterStu.Name);
}
static void SomeSideEffect(ref Student stu)
{
stu.Name = "Tom";
Console.WriteLine("HashCode={0}, Name={1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name {
get;
set;
}
}
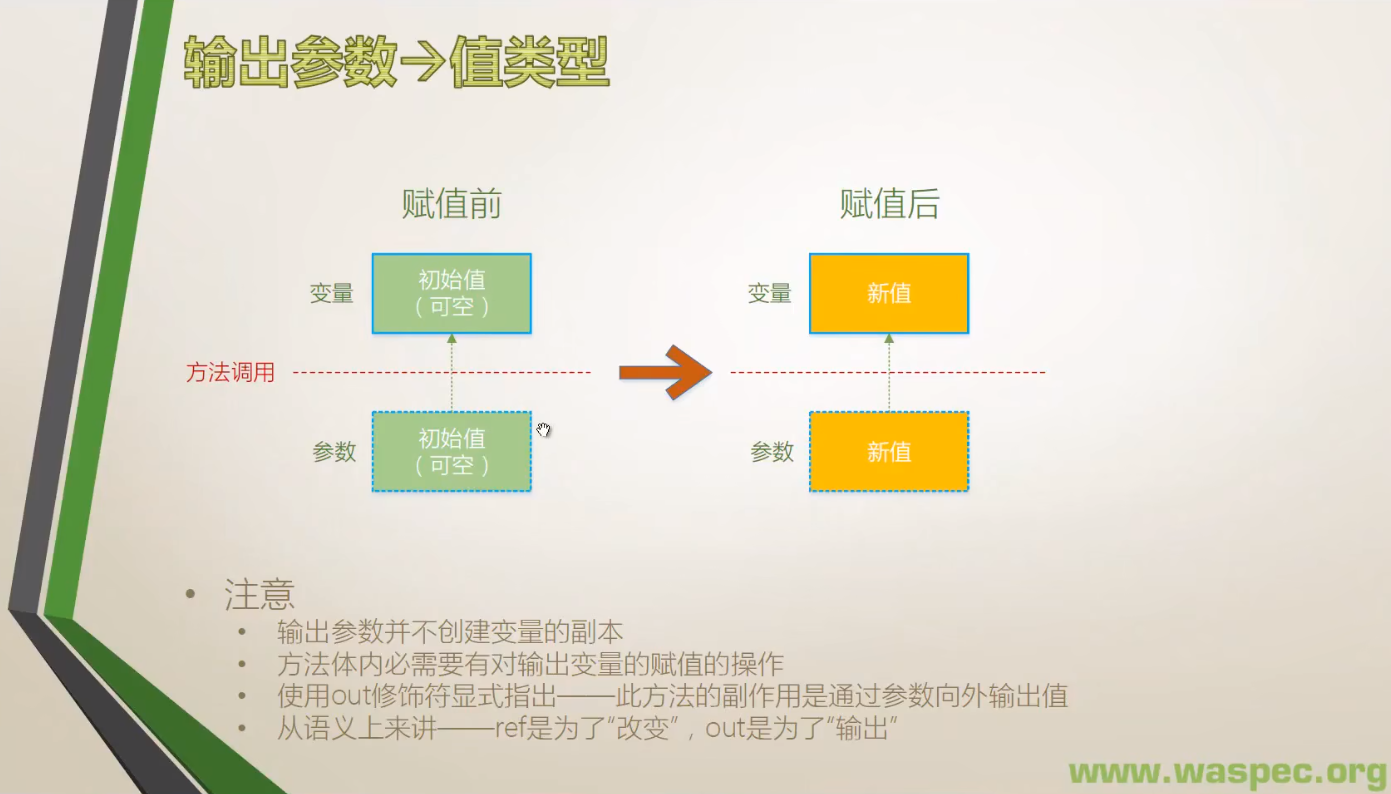
三、输出形参
- 用 out 修饰符声明的形参是输出形参。类似于引用形参,输出形参不创建新的存储位置。相反,输出形参表示的存储位置恰是在该方法调用中作为实参给出的那个变量所表示的存储位置。
- 当形参为输出形参时,方法调用中的相应实参必须由关键字 out 并后接一个与形参类型相同的 variablereference(第 5.3.3 节) 组成。变量在可以作为输出形参传递之前不一定需要明确赋值,但是在将变量作为输出形参传递的调用之后, 该变量被认为是明确赋值的。
- 在方法内部,与局部变量相同,输出形参最初被认为是未赋值的,因而必须在使用它的值之前明确赋值。
- 在方法返回之前,该方法的每个输出形参都必须明确赋值。声明为分部方法或迭代器的方法不能有输出形参。
1. 值类型
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please input first number:");
var arg1 = Console.ReadLine();
double x = 0;
if (double.TryParse(arg1, out x) == false)
{
Console.WriteLine("Input error!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Please input second number:");
var arg2 = Console.ReadLine();
double y = 0;
if (double.TryParse(arg2, out y) == false)
{
Console.WriteLine("Input error!");
return;
}
double z = x + y;
Console.WriteLine(z);
}- 实现带有输出参数的TryParse:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 0;
if(DoubleParser.TryParse("aa",out x))
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
}
}
class DoubleParser
{
public static bool TryParse(string input,out double result)
{
try
{
result = double.Parse(input);
return true;
}
catch
{
result = 0;
return false;
}
}
}2. 引用类型
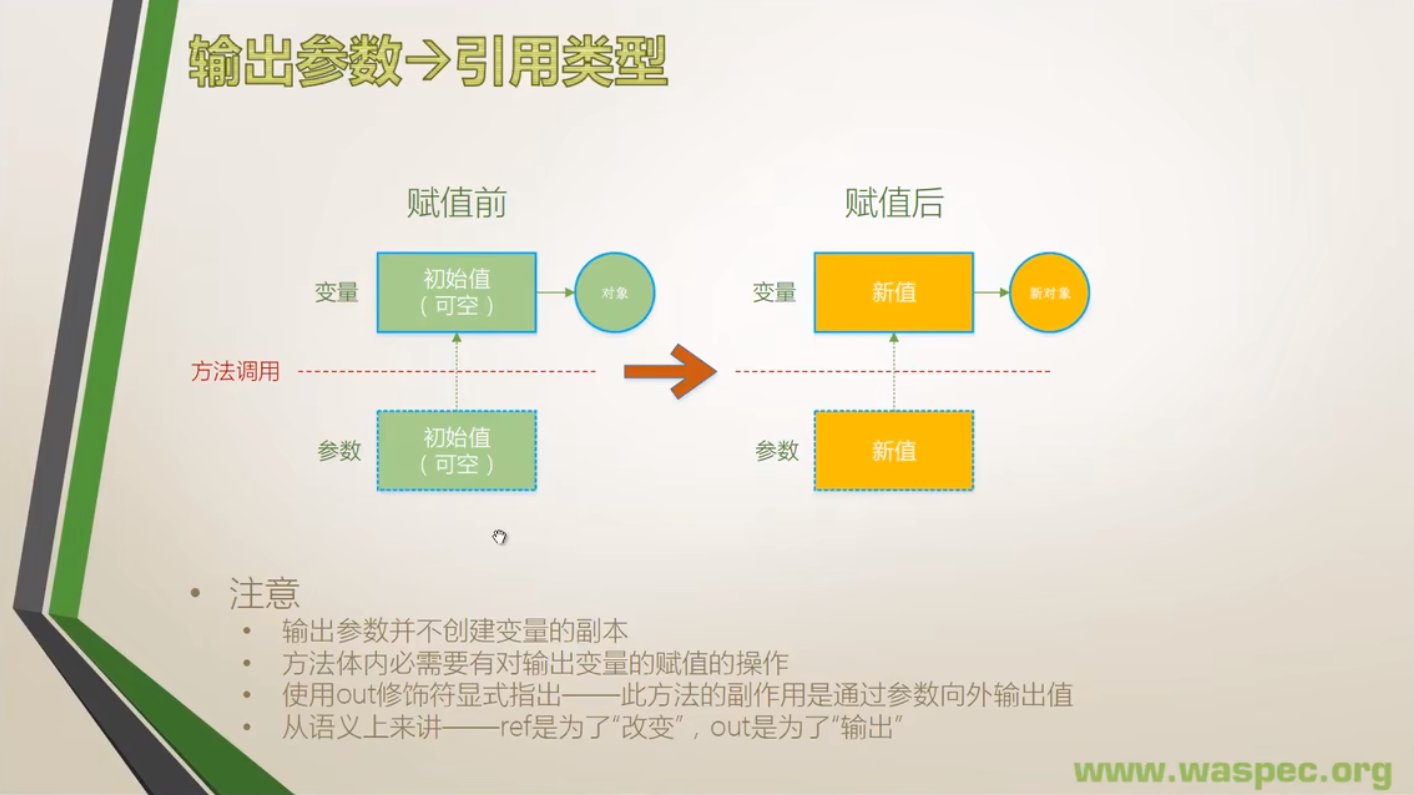
- 引用类型的输出参数实例
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = null;
if(StudentFactory.Create("Tim", 34, out stu))
{
Console.WriteLine("Student {0}, age is {1}",stu.Name,stu.Age);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int Age {
get;
set;
}
public string Name {
get;
set;
}
}
class StudentFactory
{
public static bool Create(string stuName,int stuAge,out Student result)
{
result = null;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(stuName))
{
return false;
}
if (stuAge <
20 || stuAge >
80)
{
return false;
}
result = new Student() { Name = stuName, Age = stuAge
};
return true;
}
}四、数组参数

- params会自动声明一个数组,将给出值传入数组并传给函数。常用的writeLine / Split即为数组函数,先将参数传入object / char数组,再传给writeLine / Split函数。
- 参数列表只允许有一个params参数,且必须放在最后的位置。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var myIntArray = new int[] {
1, 2, 3
};
int result = CalculateSum(myIntArray);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static int CalculateSum(int[] intArray)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var item in intArray)
{
sum += item;
}
return sum;
}
}等同于下面代码
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int result = CalculateSum(1, 2, 3);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static int CalculateSum(params int[] intArray)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var item in intArray)
{
sum += item;
}
return sum;
}
}- WriteLine / Split示例


五、具名参数

- 具名参数能提高代码的可读性
- 不再受参数列表顺序的限制
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintInfo("Tim", 34);
PrintInfo(age: 24, name:"Wonder");
}
static void PrintInfo(string name, int age)
{
Console.WriteLine("Helllo {0}, you are {1}.",name,age);
}
}六、可选参数

- 参数因为具有默认值而变得“可选”
- 不推荐使用可选参数
class Program
{
static void Main{
string[] args)
{
Printinfo();
}
}
static void Printinfo(string name = "Tim", int age = 34)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello {O}, you are {1}.", name, age);
}七、扩展方法
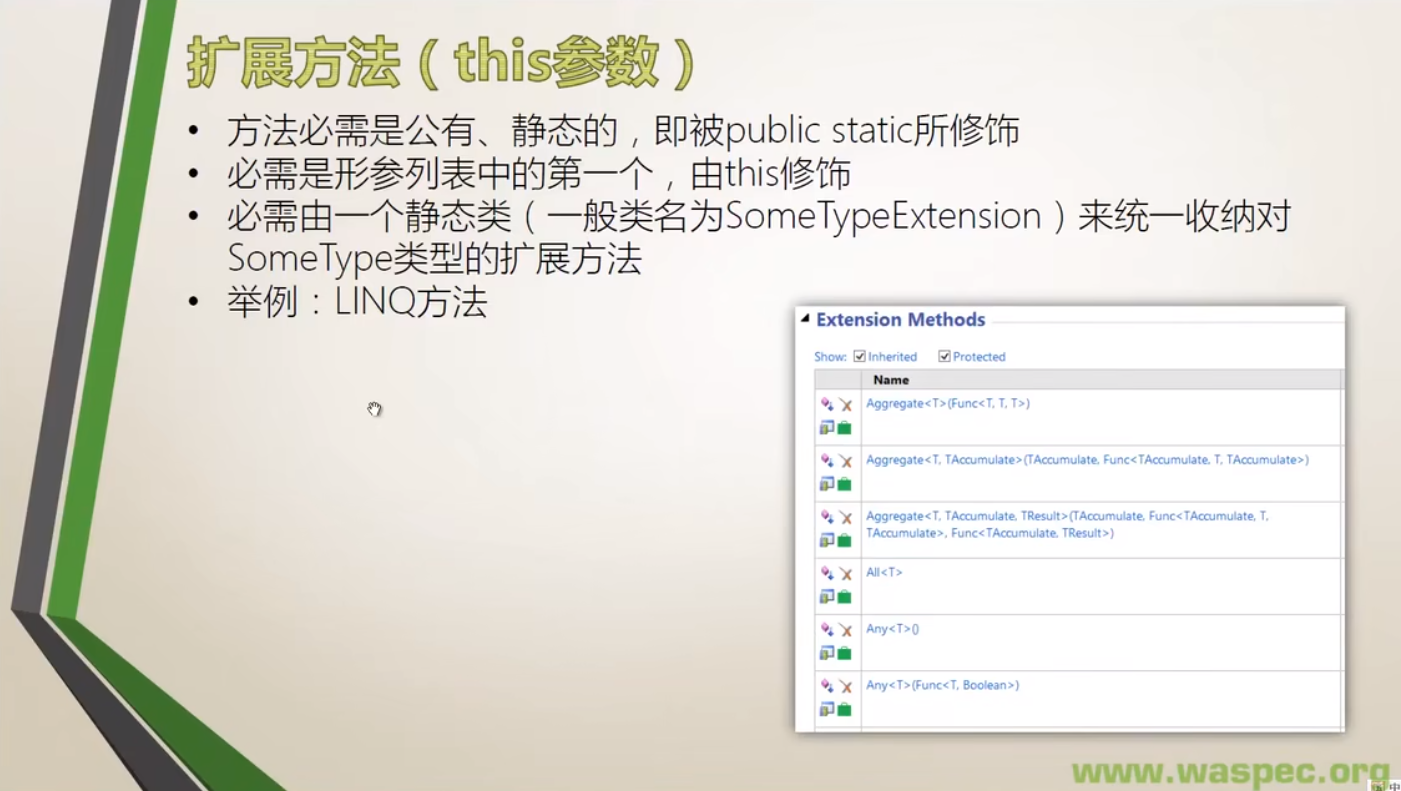
当无法对原始类进行修改时,可通过扩展方法为目标数据类型追加方法。扩展方法参数列表里第一个由this修饰,即为该参数数据类型的扩展方法。
- 无扩展方法:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 3.14159;
// double 类型本身没有 Round 方法,只能使用 Math.Round。
double y = Math.Round(x, 4);
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}- 有扩展方法:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 3.14159;
// double 类型本身没有 Round 方法,只能使用 Math.Round。
double y = x.Round(4);
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
static class DoubleExtension
{
public static double Round(this double input,int digits)
{
return Math.Round(input, digits);
}
}
- LINQ实例
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var myList = new List<
int>(){
11, 12, 9, 14, 15
};
//bool result = AllGreaterThanTen(myList);
// 这里的 All 就是一个扩展方法
bool result = myList.All(i => i >
10);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static bool AllGreaterThanTen(List<
int> intList)
{
foreach (var item in intList)
{
if (item <= 10)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}List所使用的All方法即为扩展方法,位于Linq命名空间下Enumrable静态类中。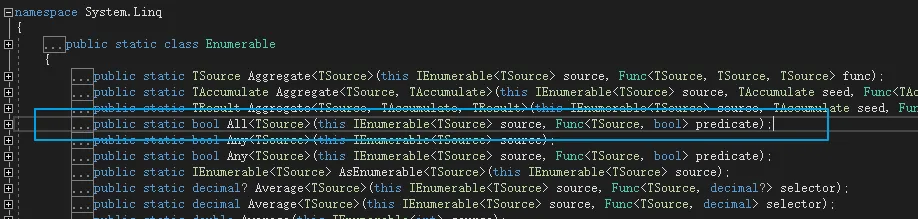
总结

