首先我们理解计算机硬件层面的缓存 (CPU Cache)。
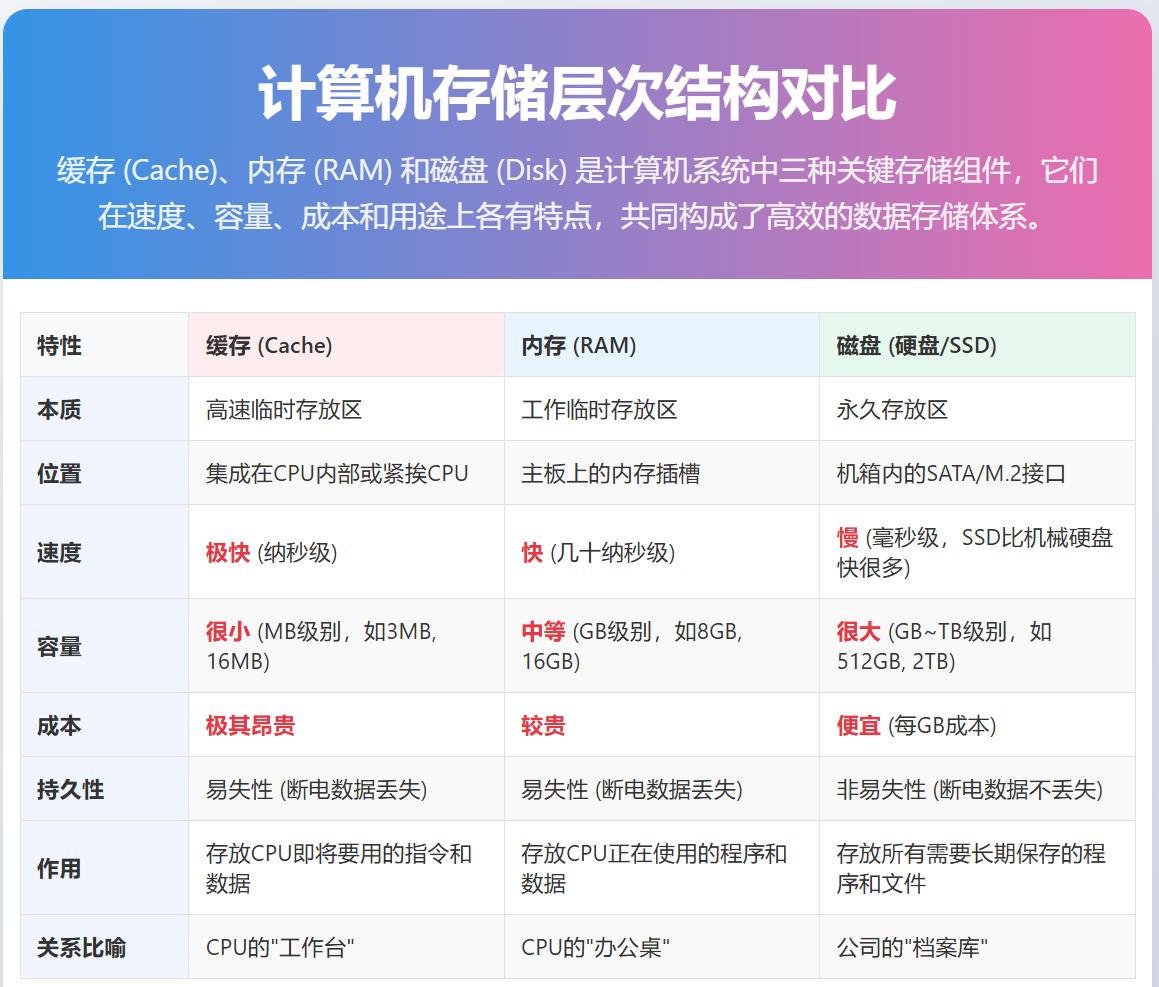
计算机存储系统是一个金字塔结构,越靠近塔顶(CPU)的部件,速度越快、容量越小、成本越高;越靠近塔底,速度越慢、容量越大、成本越低。
缓存速度最快但容量最小,用于存储CPU立即需要的数据;内存作为中间层,存储正在运行的程序和数据;磁盘提供大容量永久存储。
这种层次结构使计算机能够以合理的成本获得接近缓存速度的整体性能。
当CPU需要数据时,它首先检查缓存,如果找不到(缓存未命中),则检查内存,如果仍然找不到,最后从磁盘加载。越靠近CPU的存储层级,速度越快,但成本越高且容量越小。
Redis的数据主要存储在内存(RAM)中。
我们只是把Redis“当作”缓存系统来使用,这个“缓存”是一个软件架构层面的逻辑概念(角色)
业务流程图:


具体实现:
ShopServiceImpl
package com.hmdp.service.impl;import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
import cn.hutool.json.JSONUtil;
import com.hmdp.dto.Result;
import com.hmdp.entity.Shop;
import com.hmdp.mapper.ShopMapper;
import com.hmdp.service.IShopService;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;import javax.annotation.Resource;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import static com.hmdp.utils.RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_KEY;
import static com.hmdp.utils.RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_TTL;/*** <p>* 服务实现类* </p>** @author ztn* @since 2025-9-12*/
@Service
public class ShopServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ShopMapper, Shop> implements IShopService {@ResourceStringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;@Overridepublic Result queryById(Long id) {// 1.从redis中查询商铺缓存String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id);// 2.判断是否存在if(StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)){// 3.存在,直接返回Shop shop = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, Shop.class);return Result.ok(shop);}// 4.不存在,根据id查询数据库Shop shop = getById(id);// 5.不存在,返回错误if(shop == null){return Result.fail("店铺不存在!");}// 6.存在,写入redisstringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(shop),CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);// 7.返回return Result.ok(shop);}@Override@Transactionalpublic Result update(Shop shop) {Long id = shop.getId();if (id == null) {return Result.fail("店铺id不能为空");}// 1.更新数据库updateById(shop);// 2.删除缓存stringRedisTemplate.delete(CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id);return Result.ok();}
}